- Max Head , 160m
- Pressure, 16bar
- Temtperature, 140 °C
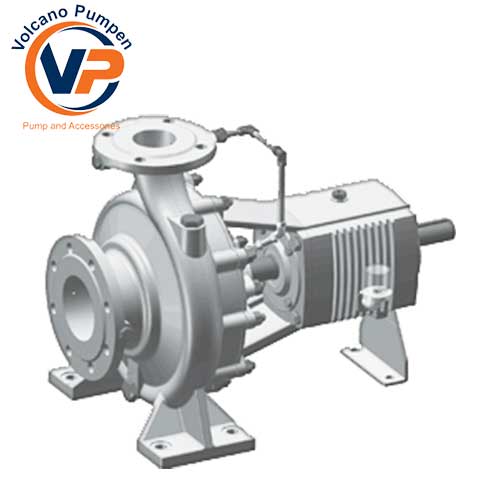
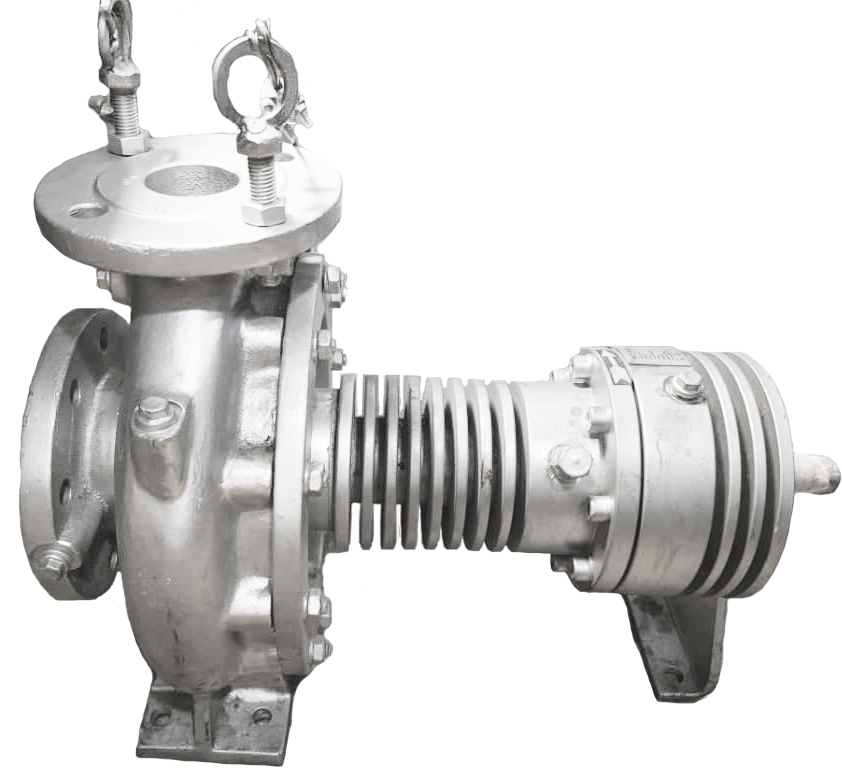







































To introduce Volcano hot oil pump, it is worth mentioning that in many industrial and refinery uses, utilizing ordinary pumps is impossible due to the use of liquids at high temperatures such as oil and even water. In this regard, it is necessary to use a heat-resistant pump. Thus, experts and engineers designed and manufacture hot oil pumps. The single flow, single-stage spiral pump that is connected to the electrical motor shaft which comes through a mechanical seal is known as Volcano hot oil pump or centrifugal pump. In a centrifugal pump, the liquid enters through the suction nozzle and then passes through the center of the pump and the propeller.
The Volcano hot oil pumps are a mechanical device that utilizes one or more drive rotors, called propeller, to harness the rotational energy and convert it to propel a fluid. The fluid in its way enters the impeller, which is spinning rapidly and is thrown out by the centrifugal force along its circumference via the tips of the impeller blades. Actually, the fluid’s speed and pressure are increased by the propeller and directed towards the pump outlet. The pump housing is particularly designed for compressing fluid from the pump inlet, conveying it to the impeller, and finally slowing down and controlling it before discharge.
Type, brand, and power are three main factors that determine the price of the hot oil pump. Additionally, specification and the manufacturing country are of a high level of importance in pump price. The hot oil pumps and linear water pumps can pump up to 350°C and 180°C respectively. These pumps’ ability to work at the aforementioned high temperatures is their main particular feature. Our experts are accessible for a hot oil pump consultant and price. Hot oil centrifugal pumps, also known as hot oil circulating pumps and hot oil eccentric pumps, of which are of the centrifugal category and are usually used to move and circulate oil or water at high temperatures.
6 types of volcano hot oil industrial pumps are utilized in the oil and gas industry
All types of hot oil industrial pumps are used to transfer fluids in the oil and gas industry. Pumps used in O&G can be classified based on their design and construction and are generally divided into 6 main categories:
Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps that are used in the oil and gas industry. These pumps use centrifugal force to enter fluids from the inlet through the rotation of the pump impeller and drive it to the discharge section. The discharge flow control valves regulate the pump flow.
Plunger or piston pumps are also common industrial pumps in the oil and gas industry. Piston pumps are based on the reciprocating motion of pistons. Pistons are utilized to push fluid in an enclosed cylinder into a piping system. Piston pumps are considered constant flow pumps since they have a constant speed, and the flow rate is constant despite the system pressure. A relief valve, an essential part of any piston pump, is used to discharge piping system pressure to prevent over-pressurization of the pump and piping system.
A progressive cavity pump is a type of positive displacement pump and is also known as an unconventional screw pump or a cavity pump. By turning its rotor, it propels the fluid, in the pump, through a series of small, fixed, discrete cavities. Progressive cavity pumps are utilized for high viscosity fluids or when the composition of the pumped fluid is not desired.
Diaphragm pumps are most widely used in industry as oil and gas pumps and transfer fluid by positive displacement with valves and diaphragms. The working principle of this pump is that reducing the volume increases the pressure in the vacuum and vice versa. Diaphragm pumps are not only suitable for high volume fluid transfer operations in oil refineries, but also, they require much less maintenance than positive displacement pumps due to fewer moving parts and less friction during operation and are available in compact designs.
A gear pump uses multiple gears to pump fluid by displacement. Gear pumps are commonly used types of positive displacement pumps for transporting industrial fluids. Moreover, another application of gear pumps is for high viscosity chemical transfer. There are two main types of gear pumps: external gear pumps that use two external gears or timing gears that stir an internal gear set. Internal gears are not in contact with each other, so external gear pumps are proper for non-lubricating fluids injection. Internal gear pumps use pinion gear to drive the internally coupled gear. Gear pumps are in the category of positive displacement (or constant displacement), this means that they pump a fixed amount of fluid per rotation.
A metering pump injects a precise volume of fluid in the defined time step; thus, it provides an accurate flow rate. Injecting fluids in the adjustable flow rate is sometimes called metering. The ”metering pump” term return to application or usage rather than the utilized pump type. Most metering pumps are simplex reciprocating pumps with a packed piston or diaphragm liquid end. Diaphragm liquid end type is preferable to reciprocating ones since pumped liquid inside the diaphragm is a seal. There is no leakage into the atmosphere.
Hot oil pumps convert the rotational kinetic energy to hydrodynamic energy of fluid flow to inject fluids. Rotational energy is often supplied by the electrical motor. They are a subset of dynamic axisymmetric turbo machines that work by absorption. Fluid enters the pump impeller along or near the rotation axis and is accelerated by the impeller and flows radially outward to the diffuser or torsion chamber (shield) where it exits.
The working procedure of the Volcano hot oil pump resembles the majority of centrifugal pumps which convert rotational energy supplied by an electrical motor to the energy in the flowing fluid. A part of energy consumes fluid kinetic energy. The fluid enters from the eyepiece of the pump body, then the fluid is rotated radially and tangentially by the impeller blades until it exits from all peripheral parts of the impeller to the spreading part of the body. The fluid velocity, as well as its pressure, increases passing through the impeller. The diffuser-shaped part or body screwlike reduces the flow rate and increases pressure.
The common applications of hot oil circulation pumps include water, sewage, agriculture, petroleum, and petrochemical pumping. Hot oil pumps, as well as centrifugal pumps, are often suitable options due to high flow rate injection capability, abrasive solution compatibility, mixing potential, and their relatively simple design. A centrifugal fan is usually utilized to run an air transfer unit. The reverse function of the hot oil pump is a water turbine that transmits the potential energy of water pressure to the mechanical rotational energy.
Hot oil pump body materials are mainly cast iron, steel, cast steel, bronze, composite materials, carbon structural steel, alloy steel, and non-metallic materials. These parameters should be considered choosing materials: strength, corrosion resistance, erosion resistance, casting and machining performance, weld repair performance, and cost.
For most liquid transportations, grey cast iron is a reasonable choice for pump housing. Grey cast iron is strong enough to withstand the pressure in the single-stage pumps. Ductile iron is widely used in the normal pressure and temperature range. In cases where grey cast iron and ductile iron are not strong enough to withstand erosion, cast iron with a high percentage of nickel is mainly used as the pump body material. Recently, a new type of corrosion-resistant nickel cast iron material (called D2W) with good welding performance has been developed, containing a minuscule amount of niobium to improve welding performance. Common austenitic cast iron usually contains 15.92% nickel and is widely used in the brine.
Gray cast iron is the most widely used cast iron and its Iranian national standard code is HT. commonly, the pump body, pump impeller cover, suspension, and clean water centrifugal pumps are made of this material and three grades HT150, HT200, and HT250 are mostly utilized. HT150 is often used for subsidiary parts such as base and back plate, pump body, pump cover, suspension, etc. more than HT200, while main parts such as impellers, spigots, bushings, etc. are usually made of HT250. The presentation of gray cast iron is different from country to country. For instant, Japan’s codename is FC, Germany’s codename is GG, and the United States codename is Cass4.
Nodular cast iron is a type of cast iron with better overall performance and its Iranian national standard code is QT. Since its mechanical properties are close to steel and its casting and processing properties are better than steel, it is usually used as a substitute for cast steel. The most common grades used are QT450-10, QT500-7, and QT600-3. Due to the limitations of casting and other reasons, the current water pump impeller is made of this material, especially the open-cutting type impeller. The DN standard describes ductile iron as GGG, and American Express called it ductile iron.
The most widely used stainless steel is austenitic stainless steel. Austenitic stainless steel is a strong corrosion-resistant material in the diluted HCl and H2SO4 fluids for the chemical injection pumps. Additionally, other ideal corrosion-resistant materials are high-alloy stainless steel (alloy 20) and double stainless steel.
In the case of corrosive and harmful petroleum products, or when the multi-stage pump outlet pressure reaches 13.8MPa, it is necessary to use cast steel or cast stainless steel. In boiler feed water pumps and many hydrocarbon applications, martensitic stainless steel is often used. Martensitic stainless steel has suitable mechanical properties and is applicable for high working pressure conditions, but its corrosion resistance is not as proper as other types of stainless steel in chemical and other corrosive environments.
Austenitic stainless steel (CF-8M, CF-3M, etc.) is often used as pump casing material. In addition, austenitic stainless steel can resist corrosion due to its high speed and is relatively easy to weld in place. High-pressure shallow water injection pumps have higher requirements for corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The pump body is made of duplex stainless steel (50% ferrite + 50% austenite). Since the cast steel strength is modified by combining other alloys, pressure-bearing parts are cast steel, mostly when the pressure exceeds 16MPa. The national Iranian standard code is ZG, the most commonly used grade is ZG230-450. Japan, as well as the United States, usually use CS to show cast steel.
It is usually divided into Katong carbon structural steel and high-quality carbon structural steel. The representative of carbon structural steel is Q235, which is mostly used in various steel plates and section steels. The representative of high-quality carbon steel is No. 45 steel, which is widely used as a pump shaft material in the absence of corrosion.
The most prominent alloy steel is Cr40, which is usually used as a material for high-strength pump shafts.
Non-metallic materials for pumps are mainly used for sealing, such as polytetrafluoroethylene, fluorine rubber, nitrile rubber, etc., among these non-metallic materials, polytetrafluoroethylene has excellent corrosion resistance as well as high-temperature resistance, and suitable for chemical pump gaskets and mechanical seals are used. It is applicable for almost all chemical environments up to 250°C. Its disadvantages are high hardness and difficulty in assembly.
Fluorine rubber is also a kind of temperature-resistant and corrosion-resistant material. The working temperature is less than 160 degrees. When the user does not have a particular need, the company’s chemical pumps all use the sealing ring of this material. While nitrile rubber is mainly used for oil resistance or static sealing for a clean water environment.
In many water pump applications, bronze material is used as the pump housing. Lead bronze is usually utilized in low-pressure small pumps, where the lead helps to seal the pump housing. However, tin bronze is applied as the centrifugal pump housing material in bigger pumps. Although Nickel aluminum bronze shows the best mechanical performance and corrosion resistance, it is costly and not competitive.
Vertical centrifugal pumps are also called cantilever pumps. They use a unique shaft and bearing configuration that allows the Volute to hang in the pond while the bearings are out of the caravan. This type of pump use “throttle bushing” rather than a stuffing box to seal the shaft. One of the most prominent applications of this pump type is the washing machine.
In the mining industry or sand production, foam is generated to separate pure minerals or tar from sand and clay. The foam contains air, which not only plugs the conventional pumps but also loses the prime. Though history, the industry has found different solutions to this problem. In the pulp and paper industry, holes are created in the impeller. Air exits the impeller from these holes and a particular outlet exhausts air to the suction tank. The impellers also can have split blades or secondary blades between primary blades. Some pumps may have a large eye, an inducer, or recirculation of pressurized foam from the pump discharge to the suction to break up bubbles.
The centrifugal pumps have two or more impellers called multistage centrifugal pumps. Impellers can be set up on one or different shafts. At each stage, the fluid is guided to the center before finding its way to the discharge on the outer diameter. To provide higher pressures the impellers should set up in the series arrangement, while to increase the flow rate the impellers should set up parallel. One of the common applications of a multistage centrifugal pump is the boiler feed water pump. For instance, a 350 MW unit requires two feed pumps in parallel. Each feed pump is a multi-stage centrifugal pump that produces 150 liters per second at 21 MPa. The whole transmitted energy to the fluid comes from mechanical energy that rotates the impeller. This can be measured in isentropic compression, which results in a slight increase in temperature (in addition to an increase in pressure).
The linear hot oil pump is installed inside the lines and in the path of the pipe and is usually utilized to compress the passing liquid. In this regard, the intake passing liquid to the linear hot oil pump continues on its way at a higher speed to reach the desired destination. Centered on the pump liquids and applications, these pumps are also made of different materials and powers.
This category of pumps is used in the food industry, thus, due to the high importance of hygiene in these centers, these types of pumps are made of steel.
Do you want to contact a branch of Volcano ?
Do you have a question about a specific product, a service enquiry or a warranty claim? If so, please contact the local sales company in your country
Our support Hotline is available 24 Hours a day: 003197010281216
